Download links
How to install The Mysterious World of Angler Fish APK?
1. Tap the downloaded The Mysterious World of Angler Fish APK file.
2. Touch install.
3. Follow the steps on the screen.
Description
Angler fish, belonging to the order Lophiiformes, are a fascinating group of bony fish known for their unique adaptations and intriguing behaviors. These creatures inhabit the depths of the ocean, primarily in the dark, cold waters of the Atlantic and Antarctic Oceans, as well as in some parts of the Pacific. The term “angler” derives from their distinctive method of hunting, which involves a bioluminescent lure that they use to attract prey.
This remarkable adaptation not only highlights their evolutionary ingenuity but also underscores the mysteries of deep-sea life. The angler fish family encompasses over 200 species, each exhibiting a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors. While they are often depicted as grotesque and fearsome due to their unusual appearance, angler fish play a crucial role in their ecosystems.
Their predatory nature helps maintain the balance of marine life in the depths where they reside. The study of angler fish offers insights into evolutionary biology, ecological dynamics, and even potential applications in biotechnology, particularly concerning their bioluminescent properties.
Key Takeaways
- Angler fish are deep-sea predators known for their bioluminescent lure and large mouths.
- They have a unique physical appearance, with a large head, sharp teeth, and a modified dorsal fin used as a lure.
- Angler fish are ambush predators, using their bioluminescent lure to attract prey in the dark depths of the ocean.
- Reproduction in angler fish is unique, with the male fusing to the female and eventually becoming a parasite.
- Angler fish are found in deep-sea habitats around the world, with some species living in the Atlantic and others in the Antarctic.
- The conservation status of angler fish is not well known, but they may face threats from deep-sea fishing and habitat destruction.
Physical Characteristics and Adaptations
The Illicium: A Built-in Fishing Rod
One of the most striking features of angler fish is the illicium, or fishing rod, which protrudes from their heads. This elongated structure is tipped with a lure that emits light due to bioluminescent bacteria residing within it. The light serves as an effective attractant for unsuspecting prey, drawing them closer to the angler fish’s wide mouth filled with sharp teeth.
Adapting to the Deep-Sea Environment
This adaptation is particularly advantageous in the pitch-black depths of the ocean, where visibility is minimal. In addition to their unique hunting apparatus, angler fish exhibit a range of body shapes and sizes that vary significantly among species. Some species can grow to be quite large, reaching lengths of up to three feet, while others remain relatively small.
Camouflage and Survival
Their bodies are often adorned with fleshy appendages and protrusions that enhance their camouflage against the ocean floor. The coloration of angler fish typically ranges from dark browns and greens to more vibrant hues, allowing them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings. This ability to remain hidden from both predators and prey is crucial for their survival in such a competitive environment.
Feeding and Hunting Behavior
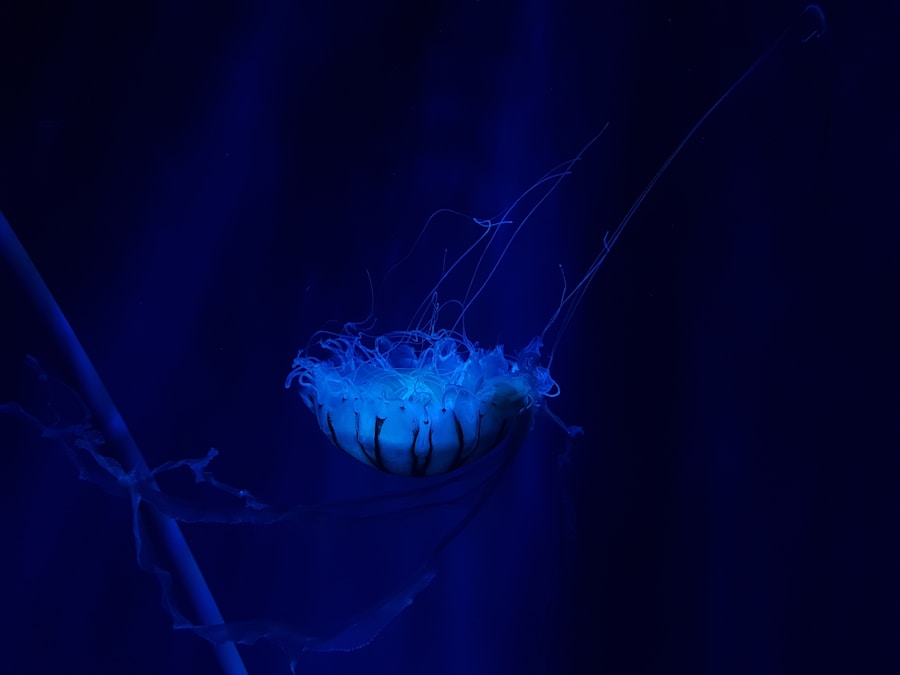
The feeding behavior of angler fish is as captivating as their physical appearance. These predators are opportunistic feeders, primarily consuming smaller fish and invertebrates that venture too close to their lure. The angler fish’s hunting strategy is a combination of patience and precision; they often remain motionless for extended periods, relying on their lure to do the work of attracting prey.
Once an unsuspecting victim approaches, the angler fish strikes with remarkable speed, using its large mouth to engulf the prey whole. Interestingly, some species of angler fish have developed specialized feeding techniques that further enhance their hunting success. For instance, certain deep-sea angler fish can expand their stomachs significantly to accommodate larger prey items.
This adaptation allows them to take advantage of infrequent but substantial meals when larger fish are available. Additionally, angler fish possess a unique jaw structure that enables them to unhinge their jaws, facilitating the capture of prey that may be larger than themselves. This remarkable feeding mechanism exemplifies the evolutionary pressures faced by these creatures in their quest for survival in a challenging environment.
Reproduction and Mating
| Species | Gestation Period (days) | Mating System |
|---|---|---|
| Elephant | 640-660 | Polygynous |
| Giraffe | 400-460 | Polygynous |
| Lion | 110-120 | Polygynous |
| Orangutan | 260-270 | Polygynous |
Reproduction among angler fish is a complex and often bizarre process that reflects the challenges of life in the deep sea. Many species exhibit sexual dimorphism, where females are significantly larger than males. In some cases, males are so small that they resemble mere parasites; they possess specialized adaptations that allow them to latch onto females for life.
This phenomenon is particularly evident in certain species like the deep-sea angler fish, where males will fuse with females, sharing blood supply and becoming dependent on them for survival. The mating process itself is equally fascinating. During courtship, males use their keen sense of smell to locate females by detecting pheromones released into the water.
Once a male finds a female, he will attach himself to her body using his modified teeth. Over time, he becomes physically integrated into her body, losing his eyes and digestive system as he relies entirely on her for sustenance. This extreme form of sexual parasitism ensures that males are always available for mating when females are ready to spawn, maximizing reproductive success in an environment where encounters can be rare.
Habitat and Distribution
Angler fish are predominantly found in deep-sea environments, typically inhabiting depths ranging from 200 meters (656 feet) to over 2,000 meters (6,561 feet). They thrive in regions characterized by cold temperatures and high pressure, conditions that would be inhospitable to many other marine species. Their distribution spans across various oceanic regions, with notable populations in the Atlantic Ocean, particularly around continental slopes and deep-sea trenches.
The habitat preferences of angler fish can vary significantly among species. Some prefer the soft sediments found on the ocean floor, where they can easily camouflage themselves and ambush prey. Others may inhabit rocky substrates or coral reefs at shallower depths.
Despite their adaptability to different environments, angler fish are generally associated with areas that provide ample opportunities for hunting while offering protection from larger predators. Their ability to thrive in such extreme conditions makes them a subject of interest for researchers studying deep-sea ecosystems and the adaptations necessary for survival in these environments.
Conservation Status and Threats

The conservation status of angler fish varies by species, with some facing significant threats due to human activities such as overfishing and habitat destruction. While many deep-sea species are not currently classified as endangered, there is growing concern about the impact of commercial fishing practices on their populations.
Additionally, climate change presents a looming threat to deep-sea ecosystems, including those inhabited by angler fish. Changes in ocean temperature and acidity can disrupt food webs and alter habitats critical for their survival. As ocean conditions continue to evolve due to anthropogenic influences, understanding the ecological roles of angler fish becomes increasingly important for conservation efforts.
Protecting these unique creatures requires a multifaceted approach that includes sustainable fishing practices and habitat preservation initiatives aimed at safeguarding the delicate balance of deep-sea ecosystems where they reside.
If you’re fascinated by the unique and mysterious world of deep-sea creatures like the angler fish, you may also enjoy reading about the FaceApp phenomenon in this related article. Just as the angler fish uses its bioluminescent lure to attract prey, FaceApp uses advanced technology to alter and enhance facial features in photos. Both subjects offer a glimpse into the fascinating ways in which nature and technology can captivate our imaginations.
FAQs
What is an angler fish?
An angler fish is a deep-sea fish known for its unique appearance and hunting method. It has a large head with a wide mouth and sharp teeth, and a bioluminescent lure that it uses to attract prey.
Where do angler fish live?
Angler fish are found in the deep waters of the Atlantic and Antarctic oceans, as well as in the waters around Australia and New Zealand. They typically live at depths of 200 to 2,000 meters.
How do angler fish catch their prey?
Angler fish use a bioluminescent lure, called an esca, to attract prey in the dark depths of the ocean. When a smaller fish or crustacean approaches the lure, the angler fish quickly snaps its jaws shut, capturing its prey.
What do angler fish eat?
Angler fish are carnivorous and primarily feed on small fish, crustaceans, and other invertebrates. They are opportunistic feeders and will eat whatever prey is available in their deep-sea habitat.
Are angler fish dangerous to humans?
While angler fish are not typically dangerous to humans, they do have sharp teeth and a powerful bite. However, their deep-sea habitat means that encounters with humans are rare.





